Soil Moisture
Measuring soil moisture
Soil moisture is vital for the environment and climate. It impacts water flow, agriculture, runoff, and droughts, helping us understand the water cycle, monitor agriculture, and manage water resources.
Soil moisture affects how water and heat move between the land and the atmosphere. Dry soil releases less moisture and heats up more, which can worsen heatwaves. Wet soil cools the atmosphere. Monitoring soil moisture from space can help predict hazardous events such as floods, droughts and heatwaves.
Abnormal weather can impact crop production and yield. This information can help predict which countries might need food aid due to severe droughts.
The video below shows the moisture levels globally. Blue depicts areas with high soil moisture, while brown shows low moisture – such as in deserts. Rainforests are green while frozen soil is white.
Credit: ESA
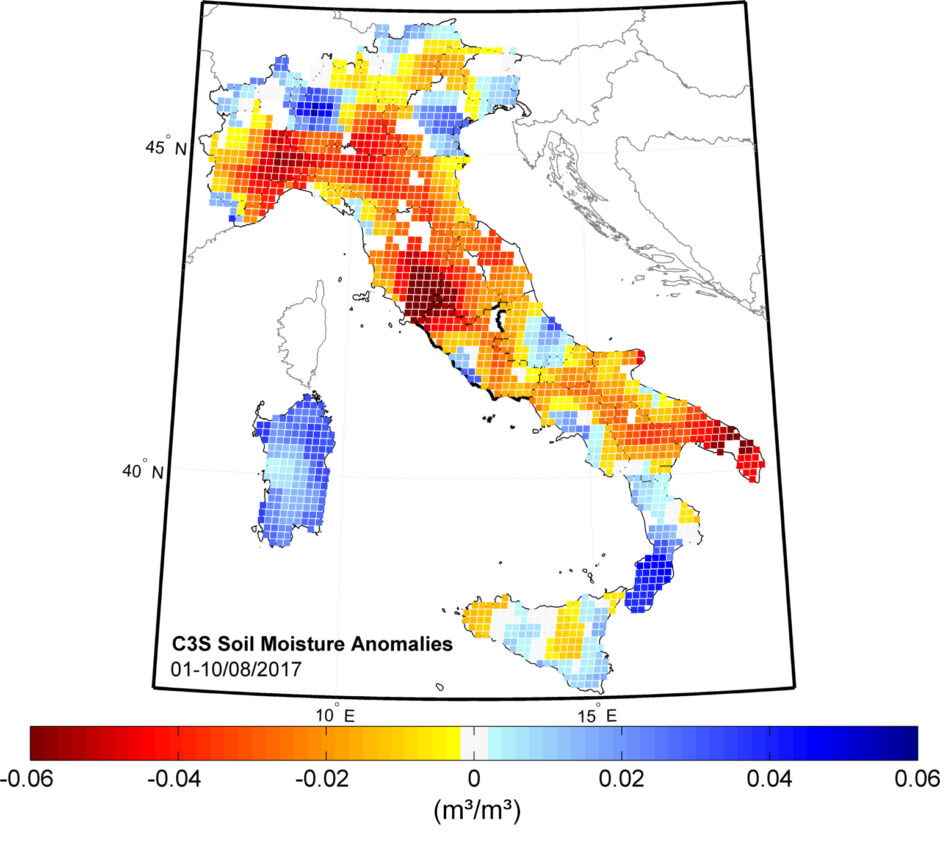
Satellite data on soil moisture show that soils in southern Tuscany have been drier than normal since December 2016. Even though drier than normal conditions occur regularly, the current situation is uniquely intense and persistent, similar to the droughts in 2007 and 2012.
Links to further information:
ESA- Nearly four decades of soil moisture data now available
